Hydrological and Hydrometeorological Systems for Europe (HYDROMET)
1996-1999
Sponsored by the EU, ENVIRONMENT & CLIMATE, DG XII
Introduction
The contribution of the National Technical University of Athens relates to the implementation of weather radar for hydrological applications, especially for spatial rainfall measurement and estimation, and consequently for storm and flash flood forecasting and warning.
More specifically the scientific goals of the project during the first year (1/7/1996 - 30/6/1997) involved research in the following areas:
- Analysis and processing of acquired radar reflectivity data sets
- Evaluation of existing conceptual rainfall-runoff models for flood-flow forecasting using weather radar data
- Development and evaluation of a fully distributed grid-based rainfall-runoff model for flood-flow forecasting using weather radar data
Conclusions
The conclusions arising from the research efforts up to-date can be summarised as follows:
- A number of storm events were analysed and processed. All rainfall patterns converted from polar co-ordinates to cartesian ones with dimensions 2x2 km2, were corrected from a variety of error sources, coming from ground clutter, abnormal beam refraction and losses, anomalous propagation and interference of signal from other than rain targets. For the conversion of the biased weather radar rainfall estimates to the unbiased ones, different approaches were examined and employed for the need to merge radar and raingage rainfall information and thus, to improve radar rainfall estimates.
- A lumped rainfall-runoff model was applied to two sub-basins of the Pinios river (Pyli and Ali-Efenti) of the Thessaly plain twice, by using as input the mean raingage rainfall derived by the Thiessen polygon method and the mean radar rainfall over the areas. Processed weather radar data merged with adequate rain-gage rainfall information can be effective for flood-flow forecasting. The rising limb and peak discharge of all stream-flow hydrographs computed from weather radar data and calibrated with rain-gage data, were more accurate than the corresponding ones of the hydrographs computed from rain-gage rainfall data alone.
- An adaptive fully distributed flood-forecasting model capable of utilising rainfall information on each grid square using weather radar, was developed. The model is able to formulate simulated hydrographs with relatively close agreement to the observed ones, as well as acceptable forecasts with a maximum lead time of four hours. The model was applied to the Pyli basin and its results were compared against the results of the HEC1F lumped model using weather radar data.
- Concerning the research work for the next period (1/7/1997 - 30/6/98), further employment and extension of the existing methods and procedures already developed for the assessment of the spatial rainfall fields, and consequently for storm and flash flood forecasting and warning will be conducted. Moreover, a Joss-type distrometer already purchased and istalled with national funds. This distrometer is initially installed in the University Campus close to the automated meteorological station and then will be transferred close to the radar site. Collaborative work with the Italian group has already been initiated in regards to the further development and application of an available rainfall-runoff model, known as the KINEROS model by using s-band weather radar data.
| Partners
|
| Coordinator |
Πανεπιστήμιο του Salford, Telford Ερευνητικό Ινστιτούτο Περιβαλλοντικών Συστημάτων |
UK |
| Partners |
Regione Veneto, Dipartimento per l' Agrometeorologia, Centro Sperimentale per I' Idrologia e la Meteorologia |
Italy |
| Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble, Ecole Nationale Superieure d' Hydraulique et de Mecanique de Grenoble |
France |
| Laboratoire d' Etude des Transferts en Hydrologie et dans l' Environnement |
France |
| National Technical University of Athens, Department of Water Resources, Hydraulic and Maritime Engineering |
Greece |
| Universitat Politecnica de Cataluna, Departamento d' Enginyera Hidraulica, Maritima I Ambiental |
Spain |
Images
 Comparison of the observed radar rainfall field (a) and the forecasted one for time step 110 min
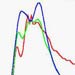 The observed hydrograph versus the computed one by using a lumped model and a distributed one (Pili Basin)
 A 4-hour flood forecasted by using the distributed model and processed radar data (Pili Basin)
|




